
MORE THAN JUST SOFTWARE –
A STRONG RELATIONSHIP WITH THE PATIENT.
ANS ANALYSIS - ANALYSIS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
What is ANS analysis?
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) unconsciously controls vital functions through the interaction of the sympathetic nervous system, which is activated in stressful situations, and the parasympathetic nervous system, which ensures recovery. Heart rate variability (HRV) reflects this interaction and serves as an indicator of the state of the nervous system.
ANS Analysis uses HRV to detect stress and imbalances in the nervous system at an early stage. Based on an ECG-accurate measurement, it records practice-relevant parameters of the autonomic nervous system.
In contrast to conventional HRV measurement, ANS Analysis enables a differentiated evaluation by integrating both HRV and specific ANS parameters. This allows a precise assessment of the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
ANS Analysis is not only diagnostically valuable, but also therapeutically applicable. Integrated biofeedback methods enable targeted stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system. This promotes an understanding of one’s own physical reactions and is intended to motivate the user to improve their stress management. Particularly in regulatory medicine, it plays a central role in the early detection of imbalances in the nervous system and the initiation of appropriate therapies.
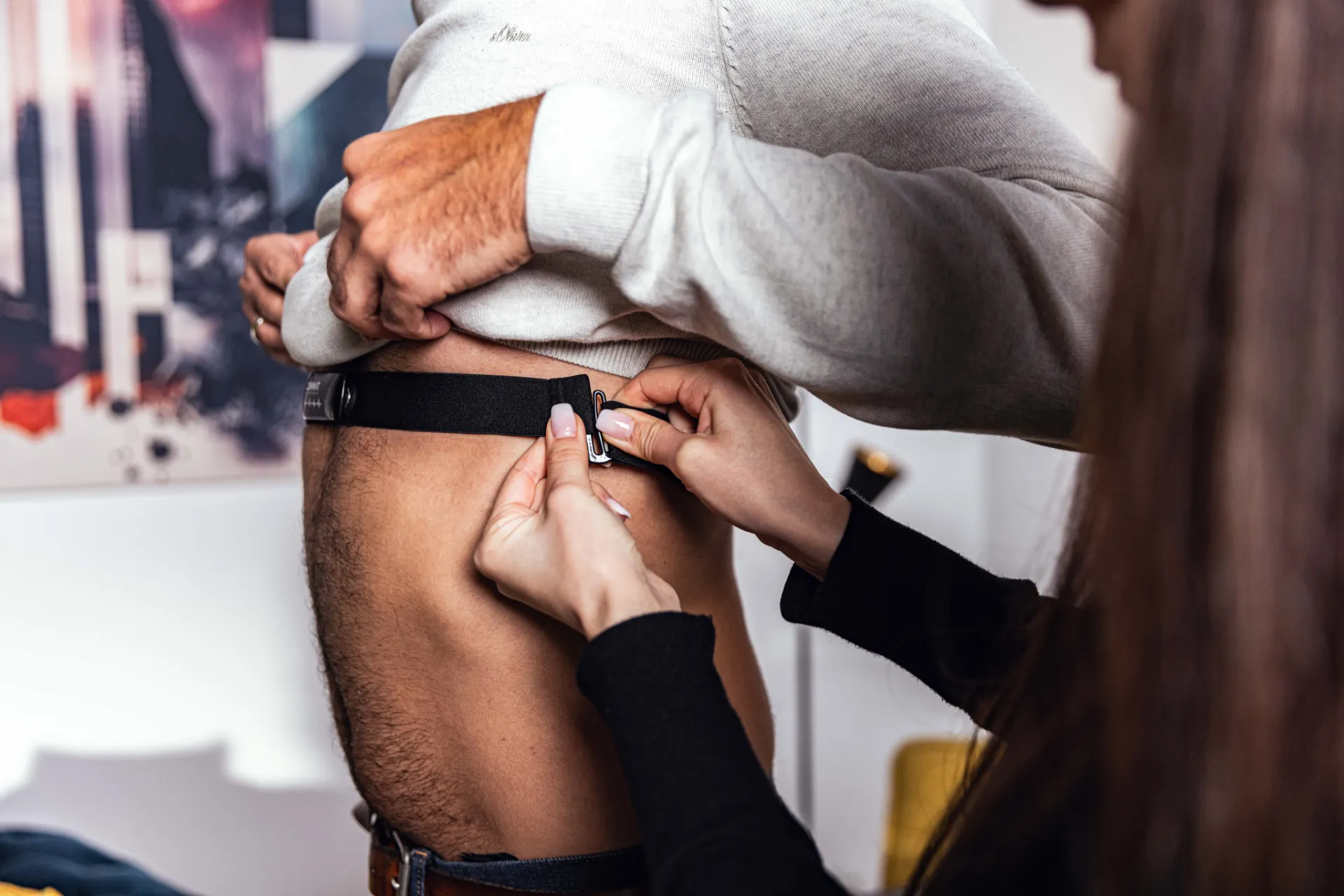
The measurement is taken via a chest wall lead, which offers an accuracy of ± 1 millisecond. This accuracy is crucial to obtain reliable data for the analysis.
How does ANS analysis work?
The evaluation is based on two main categories: HRV parameters such as rhythmogram and scatter plot, as well as specific ANS parameters such as RMSSD, stress index and alpha-1 value (DFA 1). These parameters enable a comprehensive assessment of autonomic regulation. An integrated cardiorespiratory biofeedback system supports the patient during the measurement and promotes parasympathetic stimulation. The results are displayed in an understandable way immediately after the measurement, which facilitates therapeutic communication and promotes patient compliance.
Stress and possible diagnostics simply explained:
ANS analysis as a standard examination

ANS analysis procedure
The patient should rest for about 10 minutes before the measurement. The personal data is entered. The electrodes of the chest strap are moistened.

The patient is fitted with an elastic chest strap that wirelessly records heart rate variability (HRV). The first measurement takes place while the patient is sitting or lying down in a resting situation and breathing normally. This is followed by a second measurement with a predetermined slow breathing rhythm. The examination takes about 10 to 15 minutes.

The collected data is analysed together with the patient to assess the individual state of the autonomic nervous system and their responsiveness to internal and external stimuli.
Very high patient acceptance

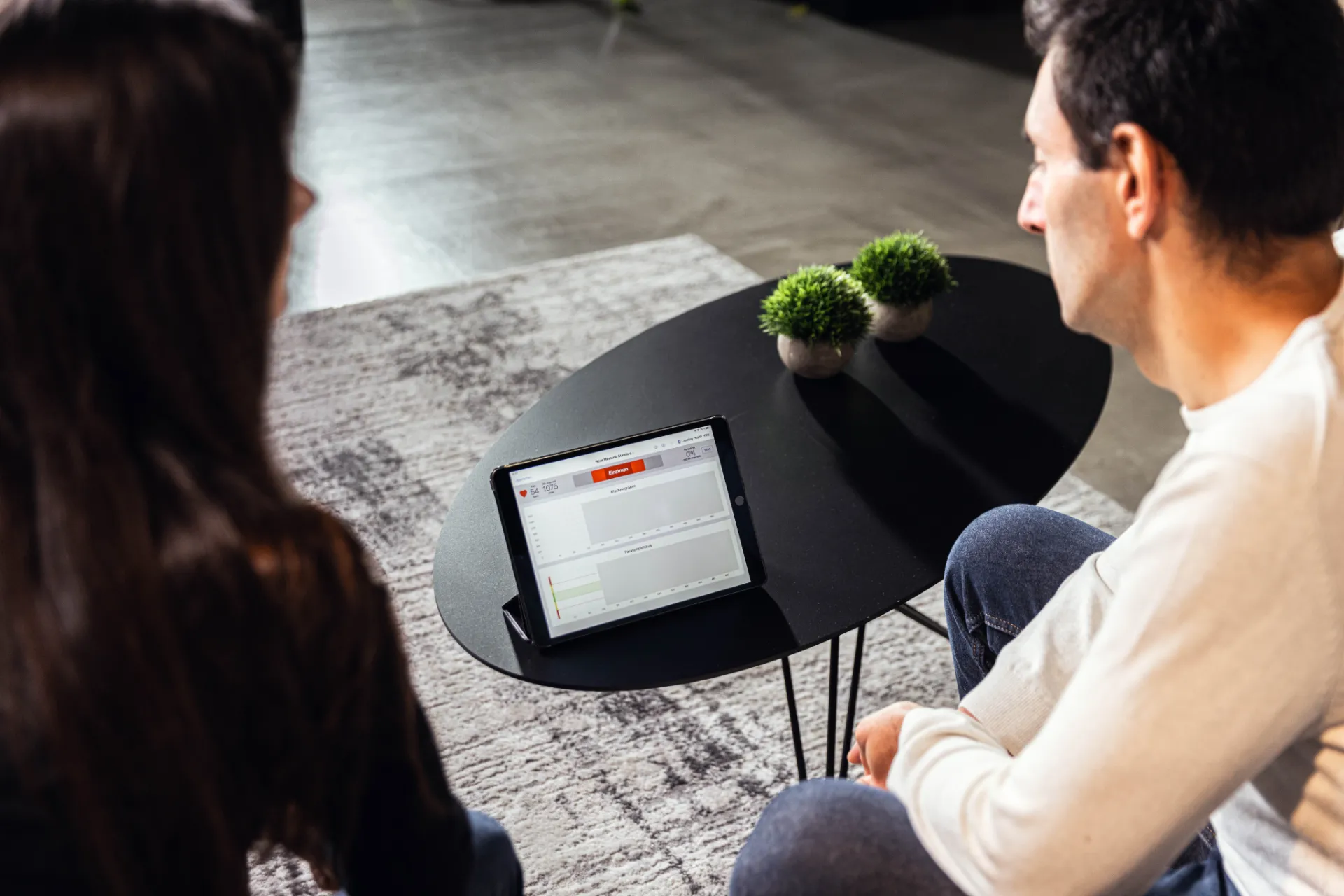
ANS ANALYSIS IN PRACTICE
ANS Analysis is a versatile tool that is used in a variety of clinical areas. It plays an important role in stress management and prevention, as it detects imbalances in the autonomic nervous system at an early stage. This is particularly relevant for the treatment of stress-related illnesses such as burnout and sleep disorders.

In cardiology, ANS Analysis allows a differentiated assessment of the possible effects of stress on the cardiovascular system. In regulatory medicine, it is used in patients with chronic illnesses such as diabetes or high blood pressure to monitor the course of the disease and evaluate therapeutic success. ANS Analysis is also gaining in importance in paediatrics, as it enables an age-appropriate assessment of autonomic regulation in children and adolescents.
Visualising regulatory capacity

Presentation and evaluation options
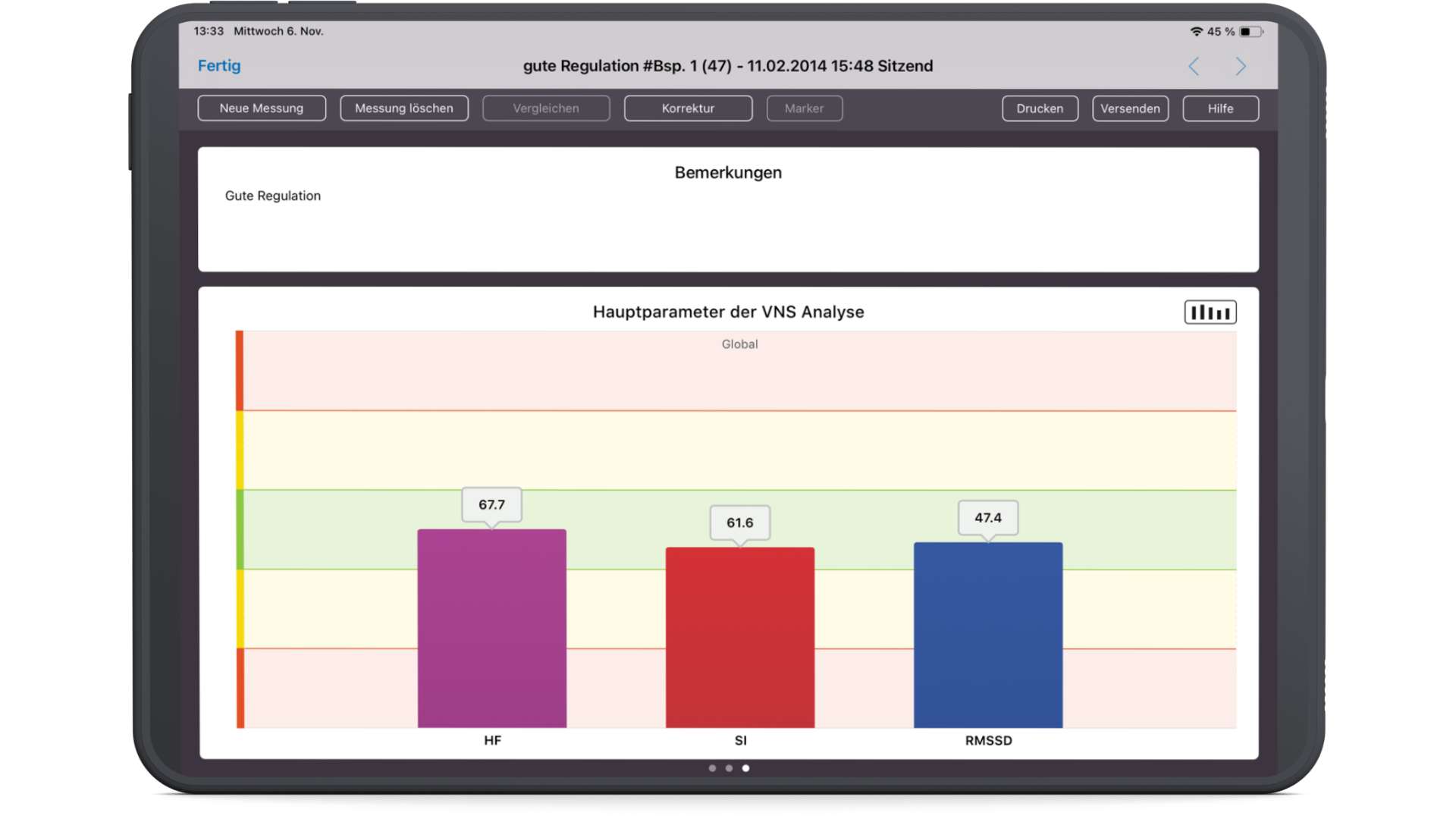
Patient view – Good regulation of the ANS
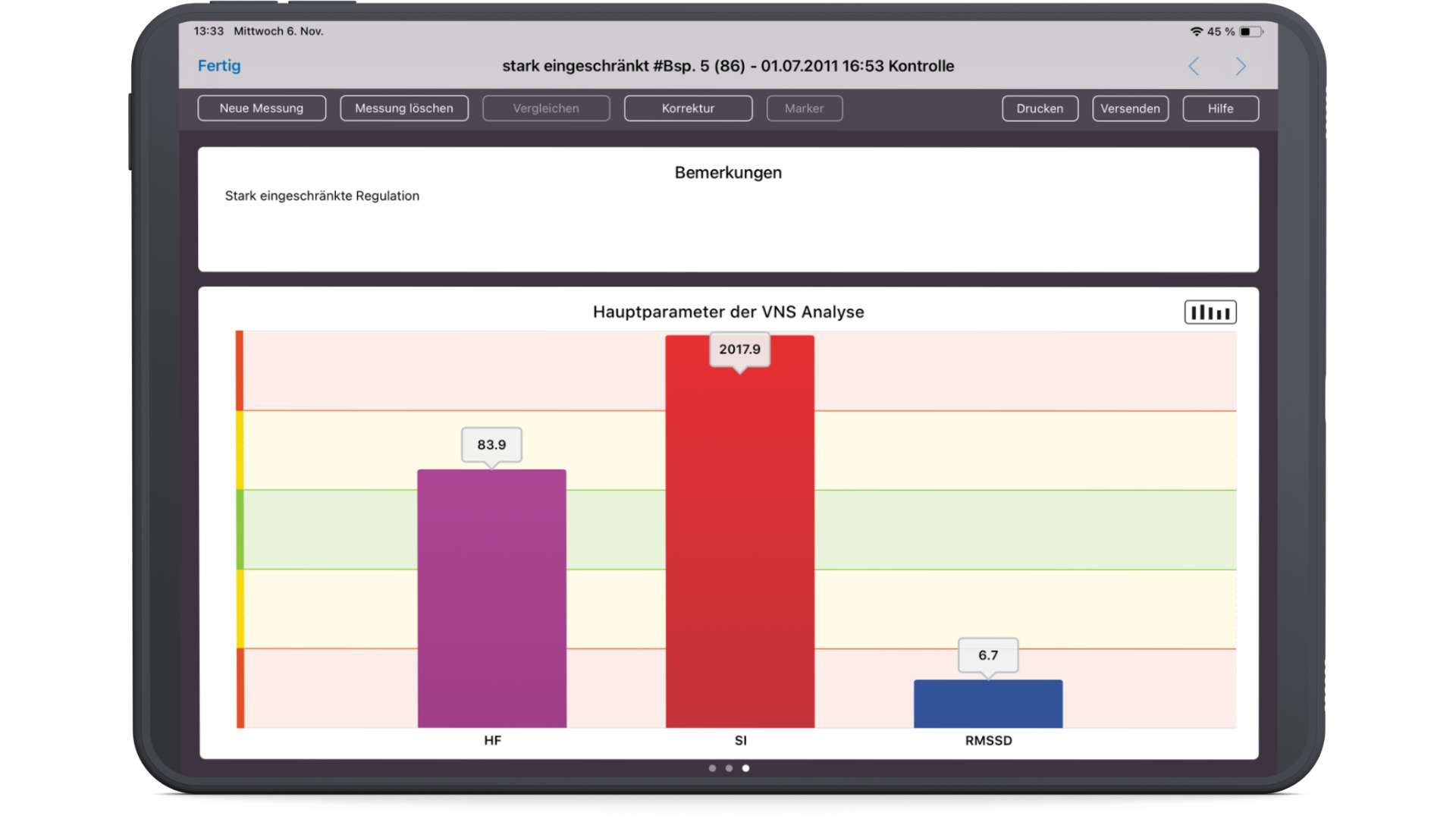
Patient view: Poor regulation of the ANS.
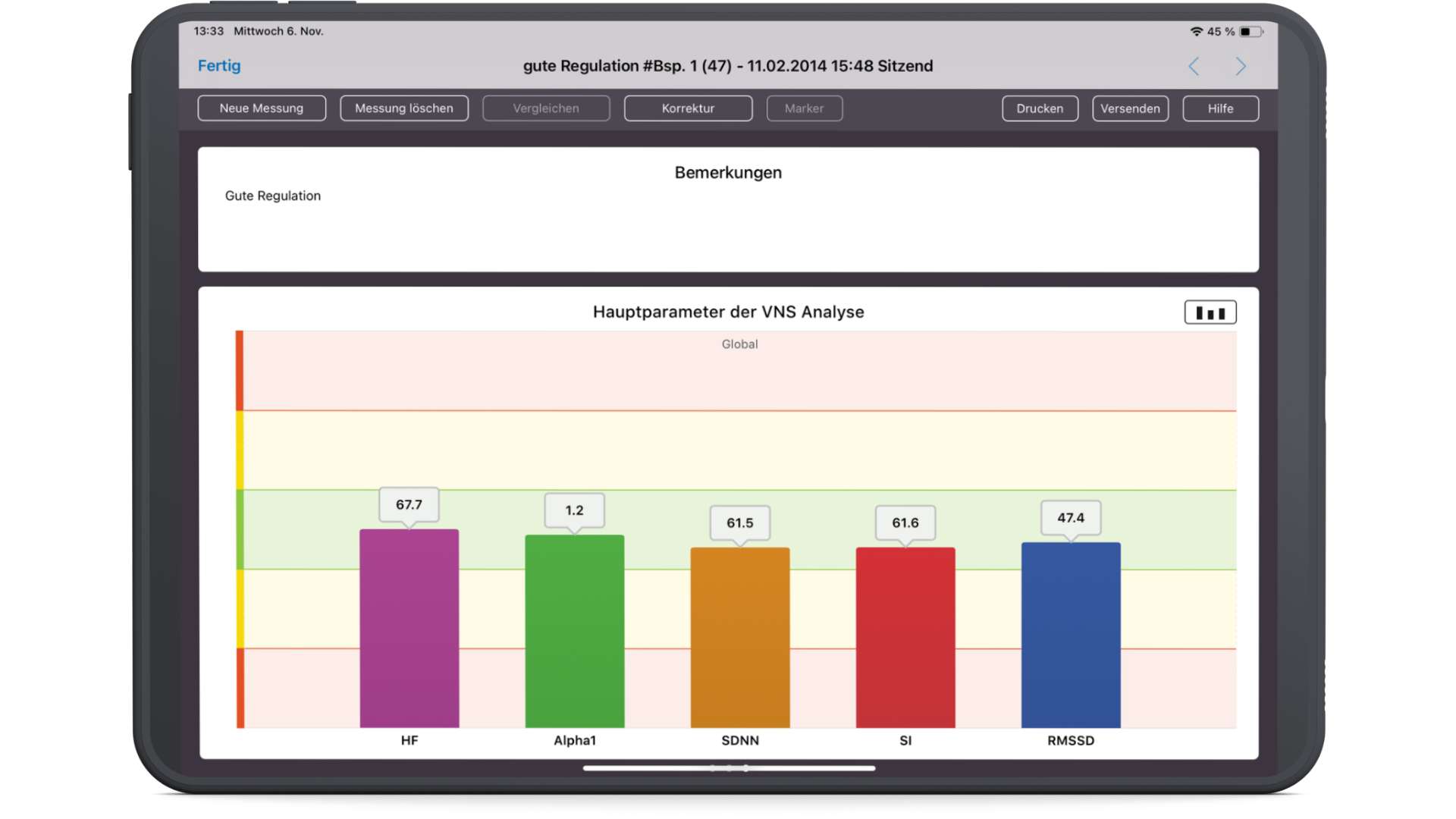
Therapist view – Good regulation of the ANS

Therapist view – poor regulation of the ANS
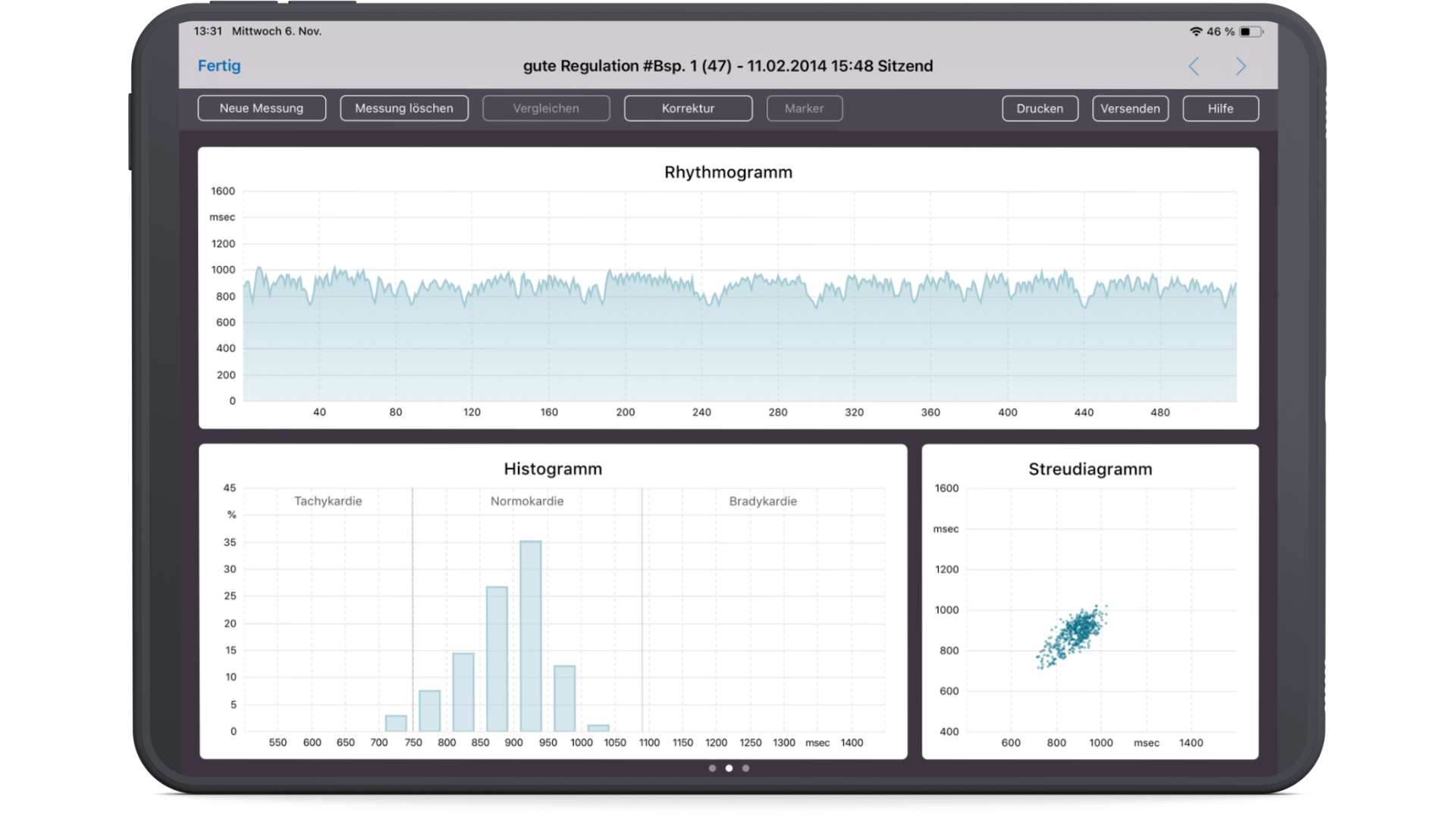
Measurement of good HRV in the rhythmogram, histogram and scatter plot
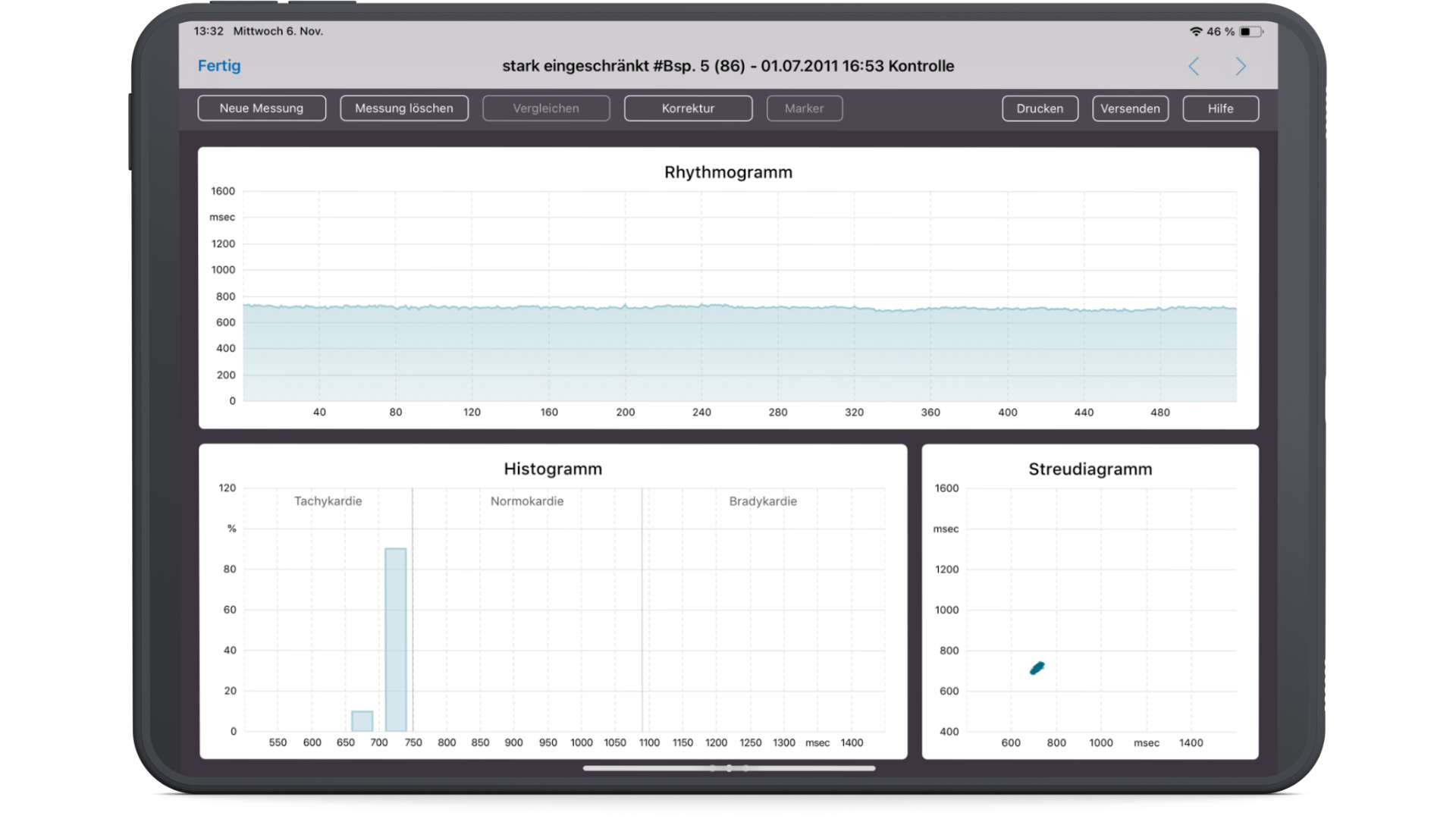
Measurement of poor HRV in the rhythmogram, histogram and scatter plot
On a scientific basis
Explanation of the analyses
The patient view explained
In the patient view, the resting pulse rate (HR, purple), the sympathetic activity (SI, red) and the parasympathetic activity (RMSSD, blue) are displayed. The color red symbolizes tension and the color blue symbolizes relaxation.
The traffic light colors in the background make it easier for the therapist to evaluate the measurement results. At a glance, the ANS Analysis shows, for example, “Everything is in the green zone” or sympathetic activity is much too high and the parasympathetic nervous system is almost no longer active. The visual display, which is understandable even for laypersons, saves time and greatly increases patient acceptance.

The therapist view explained
The therapist view can be added with a tap of the finger and is used with additional parameters for an even more detailed evaluation of the measurement results.
HR (purple) shows the average heart rate over the measured period.
Alpha 1 (green) shows the interaction of the individual autonomic control circuits and thus the quality of regulation. The alpha 1 value is used as an additive risk parameter for the patient’s prognosis.
The SDNN (standard deviation normal to normal, orange) indicates an average value of the variability and consists of sympathetic and parasympathetic components. The SDNN therefore indicates the overall variability and is also referred to as total power.
The SI (stress index according to Baevsky, red) shows the sympathetic activity.
The RMSSD (Root Mean Square of Successive Differences, blue) shows the parasympathetic activity.

The rhythmogram, histogram and scatter diagram explained
In the rhythmogram, the heart rate variability (HRV) is recorded in milliseconds. The more irregular (jagged) the rhythmogram is, the better the HRV. The flatter the rhythmogram, the worse the HRV.
The histogram is a percentage distribution curve of the measured heartbeats. A broad normal distribution according to Gaus reflects a good HRV. Few bars in the histogram indicate a limited HRV.
In the scatterplot, a point in the coordinate system results from two neighboring RR intervals. The first value is plotted on the X-axis and the second on the Y-axis. The larger the scatter cloud, the better the HRV. The denser the cloud, the more limited the HRV.
Added value through the alpha 1 value
The alpha1 value is a so-called non-linear HRV parameter and, unlike the other parameters, reflects the quality rather than the quantity of HRV. It describes the degree of correlation or similarity of the HRV data and characterizes the systemic interaction, the interplay of the individual control systems. It should be included as an additional parameter in the assessment of the overall autonomic regulatory capacity. At rest, low values (< 0.75) in particular indicate a poor prognosis and suggest that an additional diagnostic risk assessment (e.g. cardiological, oncological) is advisable. High alpha 1 values (> 1.70) indicate compensatory processes in the organism, the development of which should be monitored and observed by regular ANS Analyses. The alpha 1 value is also used as a meaningful risk parameter in intensive care units in order to be able to recognize potential risks more quickly (e.g. sepsis, MODS).
A system is a whole consisting of several individual parts. For a system to function smoothly and successfully, the individual parts must be connected, cooperate and communicate with each other.
The practical significance of the alpha 1 value can be explained very well using the example of football. In this system (team) there are players in attack and in defense. The attack (sympathetic nervous system) and the defense (vagus) must not only master their actual task (scoring goals – preventing goals), but they must also know each other, they must know what the characteristics and peculiarities of the other players are, which connections exist for the quick switch from defense via the midfield to attack. Communication and mutual understanding must be guaranteed if this team (system) is to be successful. It’s not just the statistics – the quantity (number of shots on goal, shots blocked, percentage of ball possession, etc.) that are decisive for victory or defeat. The quality of the team play is also largely responsible for success. Even a world selection with the best players is no guarantee of success against a well-coordinated team.
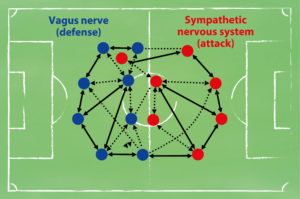
If a system, such as the autonomic nervous system, works very well together in its complexity, you have an ideal alpha 1 value of around 1.0. The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems thus work together in the best possible way for physiological regulation of the entire organism.
4 -10 breaths per minute
Cardiovagal biofeedback
Influence of breathing on autonomic regulation
Respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA) describes the breathing-dependent fluctuations in heart rate (frequency increase during inspiration, frequency slowdown during expiration). When the cardiovascular system is rhythmically stimulated by timed breathing with a frequency of six breathing cycles per minute, there is a significant increase in heart rate fluctuation and an improvement in autonomic regulation. This controlled breathing is also known as cardiorespiratory or cardiovagal biofeedback. This method can be used to determine within a few minutes whether autonomic regulation can be improved immediately by existing parasympathetic reserves or whether there is a more lasting regulatory disorder that requires further diagnostics and therapy.
The cardiovagal biofeedback function integrated into the ANS Analysis can be used both diagnostically and therapeutically. If the first measurement shows a regulatory disorder (increased sympathetic nervous system, decreased parasympathetic nervous system), a second measurement with timed breathing should be carried out immediately afterwards in order to visualize the parasympathetic reserves and the degree of regulatory ability. The ANS Analysis provides the patient with the inhalation and exhalation phase via a visual and/or acoustic signal (Fig. above and below).
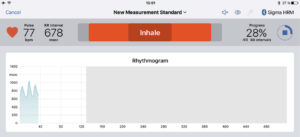
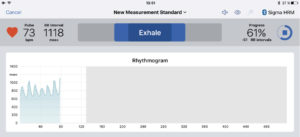
After completion of the second measurement under breathing instructions, this is compared with the first (Fig. below). The first measurement shows an increased sympathetic nervous system and a decreased parasympathetic nervous system. The second measurement was carried out while the patient was breathing and shows a clear improvement in autonomic regulation.
Through simple visualization, the patient understands why breathing training is important and what effects can be achieved with it. In this case, it is advisable to start breathing training with the Vagusvit© breathing trainer app in order to train the autonomic regulation ability and stress resilience in the long term.
With standard values for children

Study-based standard values for children
Stress is the greatest health risk of the 21st century, according to the World Health Organization. However, stress is not only an issue for adults, but is now increasingly affecting children and young people. Stress factors such as exam nerves, poor grades, the high performance demands at school, the daily pressure of deadlines, but also conflicts within the family, arguments with friends or the pursuit of social recognition have a negative impact on the body and lead to complex clinical pictures and increasing visits to therapeutic practices.
As the autonomic regulation of children and adolescents differs considerably from that of adults, the use of autonomic functional diagnostics in children was previously only possible to a limited extent.
The ANS Analysis is the world’s first system to integrate study-based pediatric reference values after a research phase lasting several years. The new update supplements the existing standard values of 20 – 80 years with the age of 10 – 19 years and now makes it possible to assess the autonomic nervous system in children and adolescents, to record their stress resilience and regenerative capacity and to prevent the stress cycle in good time, which sooner or later leads to illness.
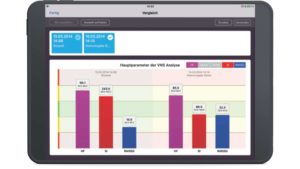
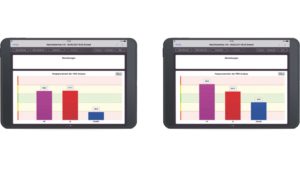
To illustrate the importance of correct standard values for children and adults, the graphs below show the measurement of a 14-year-old girl. The first figure (left) shows the measurement with the adjusted standard values for 10 – 19 year olds and the second figure (right) with the previous standard values for adults, which the 14 year old girl assessed as false positive. The adjusted standard values for children clearly show the urgent need for action.
Charles Dawin

ADDITIONAL MODULES
APPLICATION OF ANS ANALYSIS

Additional orthostasis module: In the event of conspicuously high parasympathetic values and mood disorders such as exhaustion and lack of energy, this module allows you to test your adaptability and identify possible weaknesses at an early stage. In contrast to guided breathing, which can be used to control the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system, the orthostasis test exerts a stress stimulus that can be used to control the deactivation of the parasympathetic nervous system.
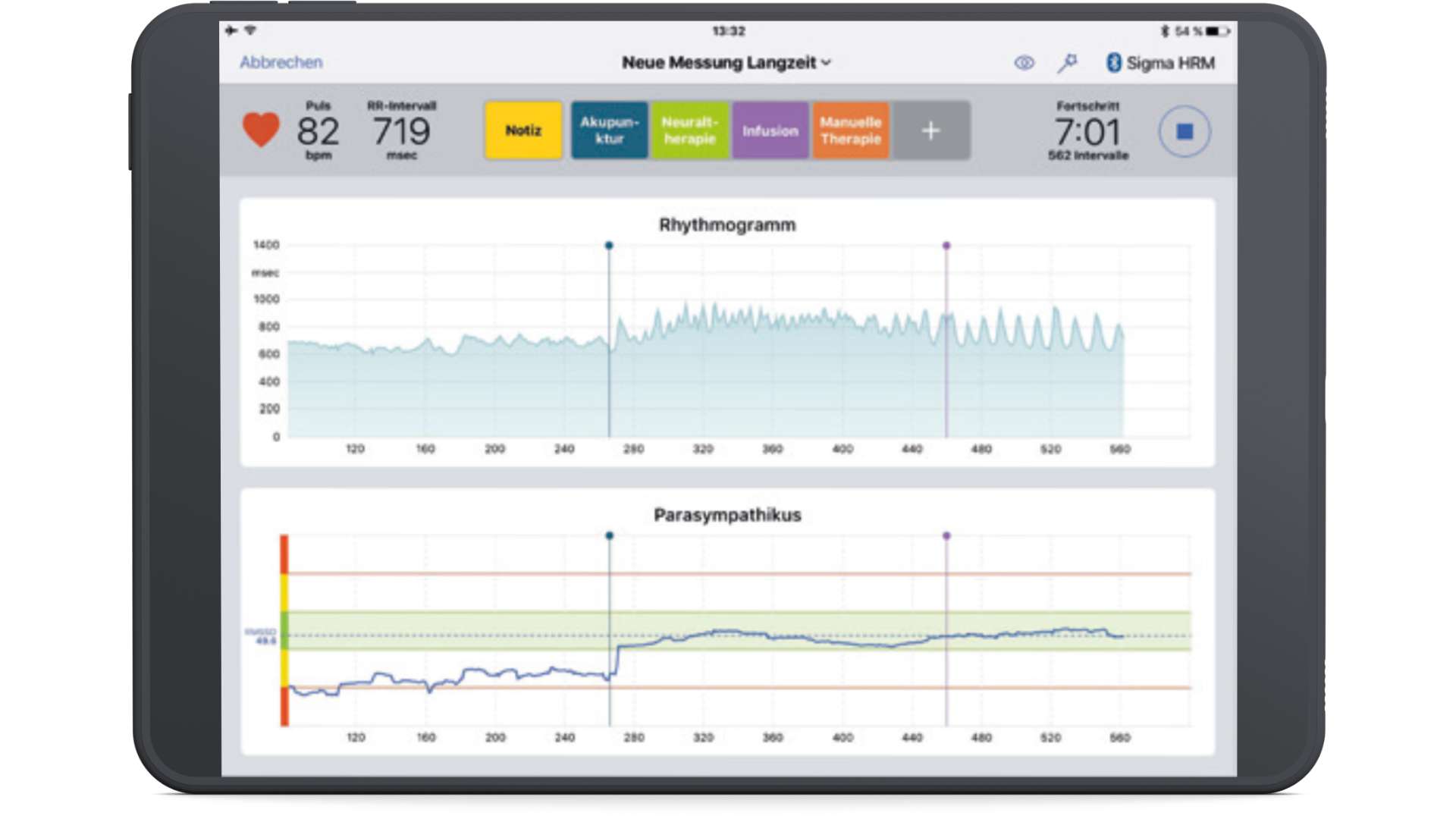
Additional long-term module: This module enables measurements to be taken for an unlimited period of time. In addition to the display of heart rate variability, parasympathetic activity is visualized in real time as a blue line. With the special marker and note function, individual markers can be created and set before and during the measurement. The effect of therapeutic interventions on the autonomic nervous system can thus be visualized for even more detailed therapy control during the measurement.
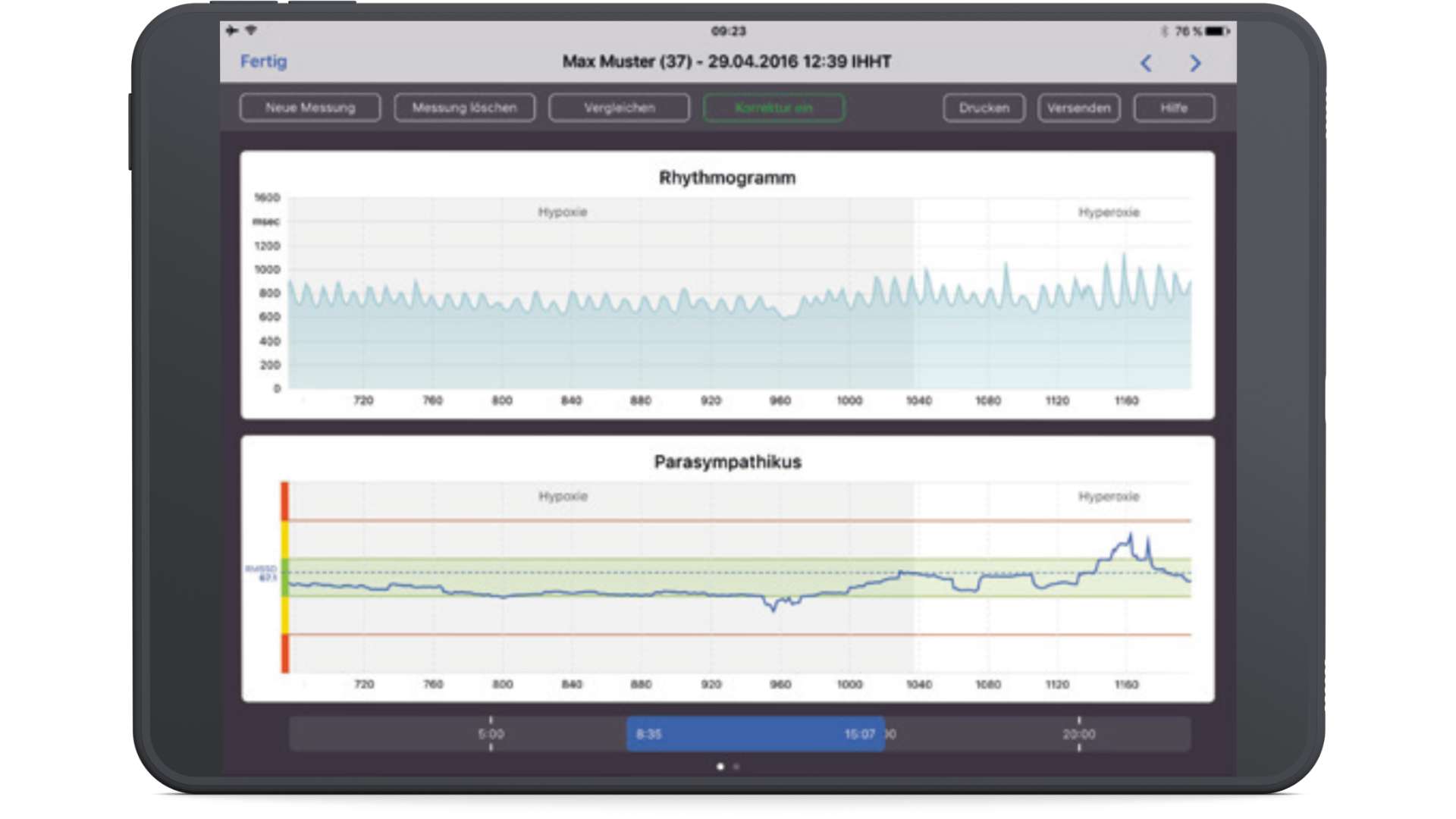
IHHT add-on module: The IHHT (interval hypoxia-hyperoxia training) add-on module makes it possible to measure parasympathetic activity in real time during an IHHT session. As the autonomic nervous system reacts directly and variably to hypoxia, the intensity of the training and the duration of the hypoxic and normoxic/hyperoxic intervals should be adapted to the ANS regulation.
100 % delegable

ADVANTAGES OF ANS ANALYSIS
AT A GLANCE
High accuracy
The ANS Analysis is based on ECG-accurate measurement and regular validation with scientific standards, which ensures reliable and precise results.
Practical relevance
Thanks to its simple handling and fast results, the ANS Analysis is ideal for the hectic daily routine in the practice.
Automatic correction functions
The ANS Analysis automatically detects and corrects technical artifacts and rhythm disturbances for a reliable evaluation of the measurement parameters.
Integrated biofeedback
Real-time visualization supports therapeutic application and promotes patient compliance with stress management techniques.
Comprehensive support
Users benefit from fast and well-founded feedback for questions regarding the interpretation of measurement results.
The better the heart rate variability
More than 2,000 satisfied users
of the ANS analysis

DR. MED. THOMAS RAU, CHIEF PHYSICIAN AND MED. DIRECTOR OF THE SONNEBERG BIOMEDICAL HEALTH CENTER “The topic of HRV as an indicator of the autonomic nervous system is a completely new approach for most doctors and has brought us new approaches for the assessment and treatment of chronic patients at the clinic. We use various systems, up to 48-hour measurement. The ANS Analysis is by far the simplest and most practical. It provides practitioners with insights into the causes and effectiveness of treatment for chronic and “unclear” diseases. The device therefore belongs in every modern practice for biological medicine.”

DR. MED. SIDDHARTHA POPAT, GENERAL MEDICINE, 1st CHAIRMAN OF IGAF E.V. “An ANS Analysis is carried out on my patients at every check-up. If this is conspicuous, my colleague immediately carries out a check under respiratory intervention. In this way, I can detect disturbances in my patients’ stress resilience and regulatory capacity. It is also an ideal tool for objectively demonstrating the effectiveness of acupuncture and neural therapy on the autonomic nervous system, which leads to an increase in patient compliance.”
Billing via the insurance

Optimally complement the ANS analysis
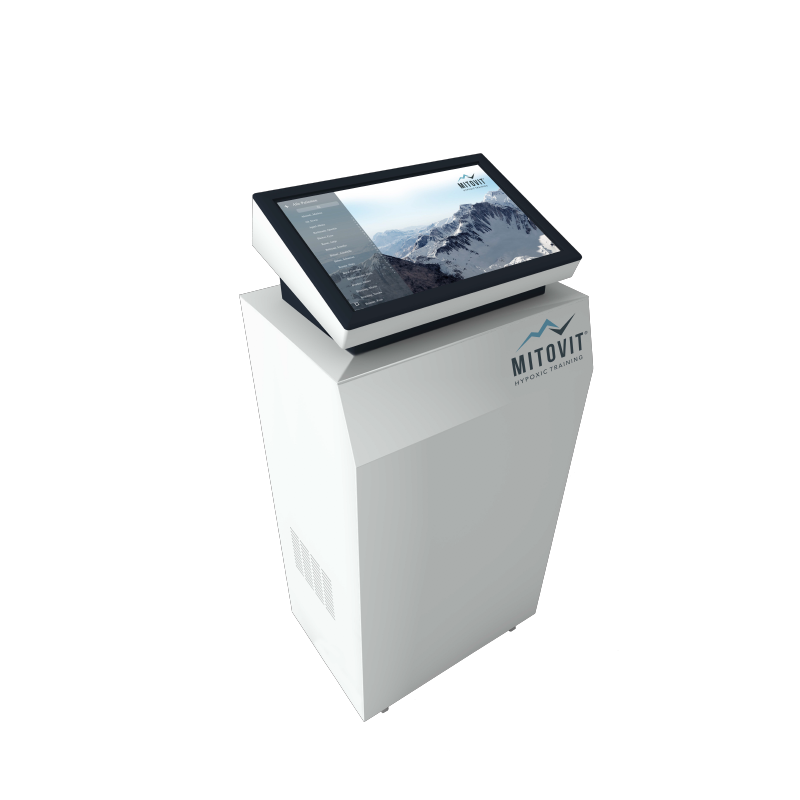

MITOVIT® Hypoxic Training: The MITOVIT® device is an innovative training system designed to harness the benefits of hypoxia for health and performance. Hypoxic training, also known as high altitude training, is based on the controlled reduction of the oxygen content in the inhaled air, which can cause positive physiological adaptation reactions in the body.
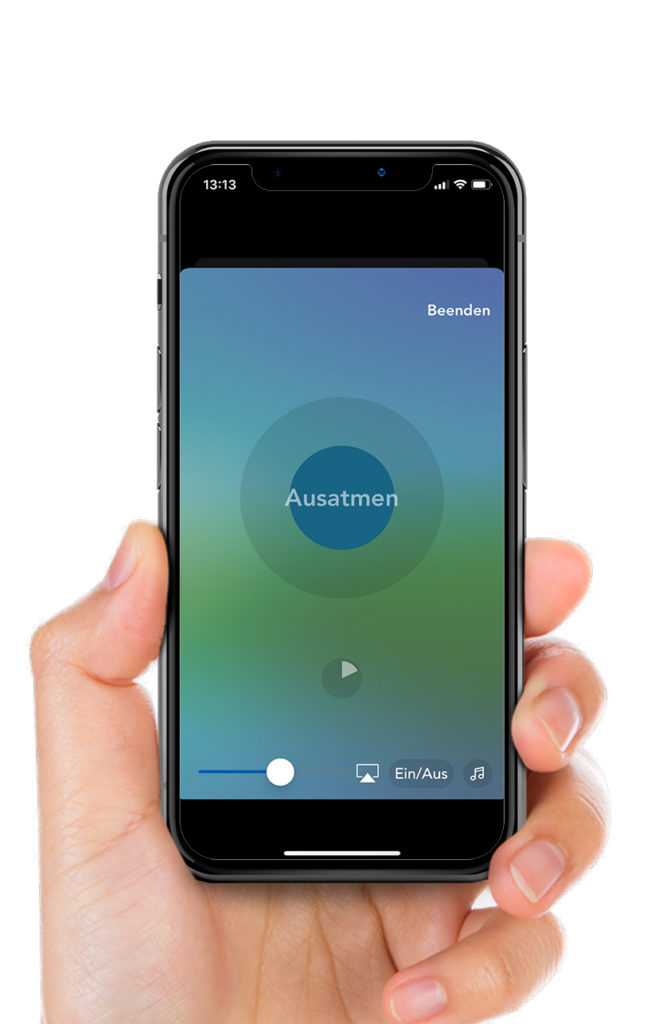
Vagusvit® breathing trainer app: The Vagusvit® breathing trainer is an app for targeted stimulation of the vagus nerve through breathing rhythms. It makes it possible to activate the relaxation nerve at any time and from anywhere using specific breathing rhythms – such as inhaling for 4 seconds and exhaling for 6 seconds.

STRESSRESIST food supplement: STRESSRESIST aims to support your stress resistance. It contains a carefully balanced combination of five high-quality plant extracts and essential B vitamins that are unique in their composition.

Accessories: Our accessories store offers chest straps and other equipment for your ANS Analysis.
GET A FREE CONSULTATION FROM US.
Contact
COMMIT GmbH
Dieselstraße 7
38259 Salzgitter




